Bipartite Graph Community Detection
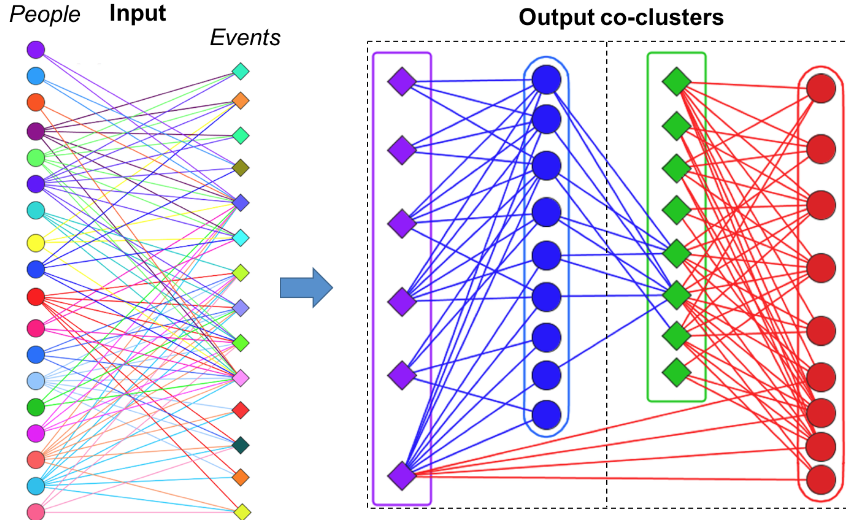
Heterogeneous graph-theoretic modeling has become an important part of biological network science, owing to the variety in data sources. Analyzing the interrelationships between genes vs. diseases, proteins vs. drugs, transcriptome vs. metabolites, predators vs. preys, or hosts vs. pathogens – all such relationships can be modeled in the form of a bipartite graph.
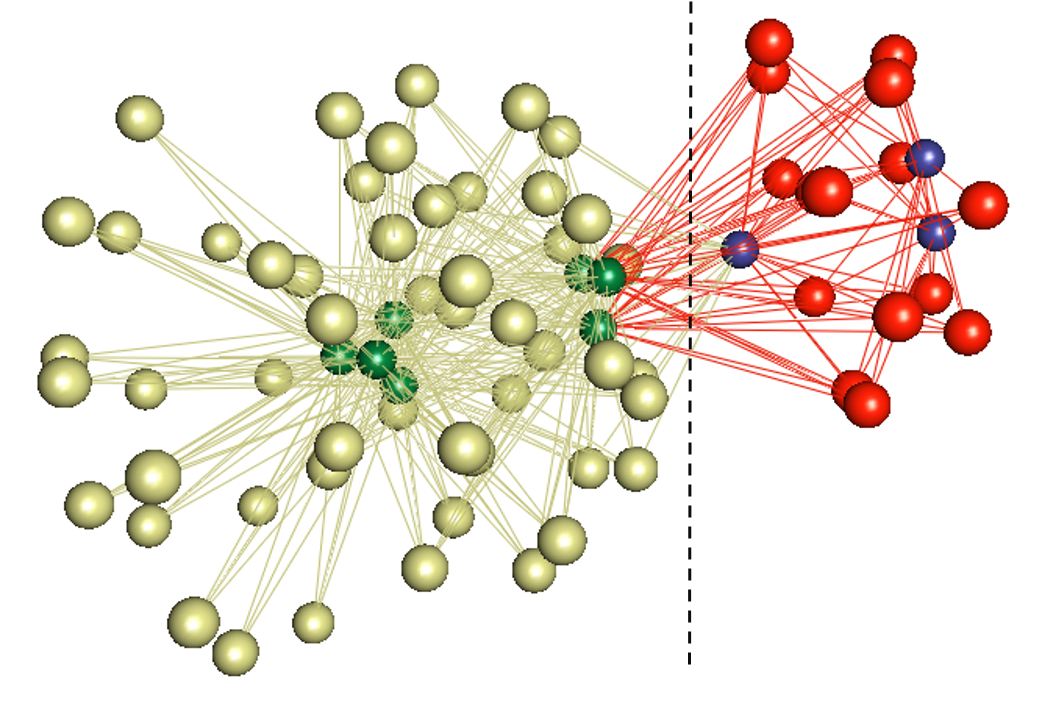
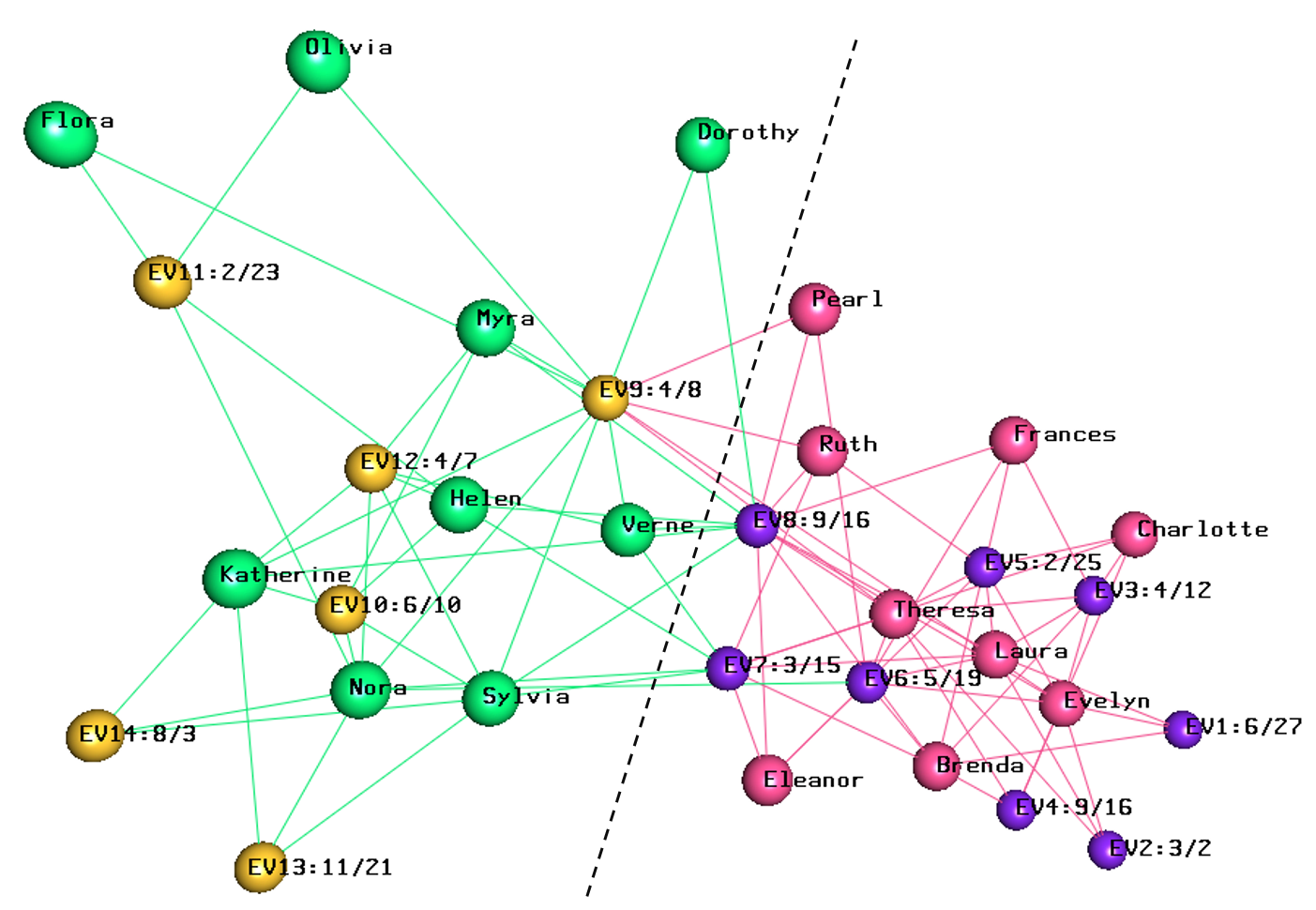
biLouvain is a bipartite graph community detection tool. As part of this work, we defined a new modularity-based metric (which we call Murata+) that can serve as an objective function for bipartite community detection; and designed an efficient algorithm to detect communities from such networks based on the metric.
Our findings show that:
- this problem is more time-consuming than the standard graph version of the problem;
- biLouvain is able to achieve between one to four orders of magnitude speedup over state-of-the-art. We have also extended biLouvain to work for cases where there are intra-type edges (in addition to the inter-type edges of a classical bipartite graph).
Thesis Project - Advisor: Ananth Kalyanaraman, Ph.D.
Representative Papers:
- Efficient detection of communities in biological bipartite networks. P. Pesantez, A. Kalyanaraman. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics (TCBB), In Press, 2017. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2017.2765319.
Software:
- biLouvain in GitHub repository